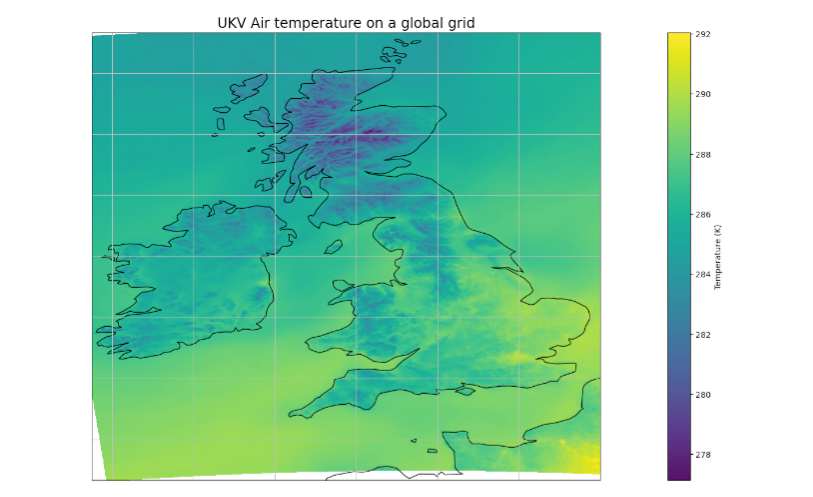
Met Office UKV high-resolution atmosphere model data
How to run¶
Running on Binder¶
The notebook is designed to be launched from Binder.
Click the Launch Binder button at the top level of the repository
Running locally¶
You may also download the notebook from GitHub to run it locally:
Open your terminal
Check your conda install with
conda --version. If you don’t have conda, install it by following these instructions (see here)Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/eds-book-gallery/1b8921af-e77f-4ccf-ae38-4813cdceba0f.gitMove into the cloned repository
cd 1b8921af-e77f-4ccf-ae38-4813cdceba0fCreate and activate your environment from the
.binder/environment.ymlfileconda env create -f .binder/environment.yml conda activate 1b8921af-e77f-4ccf-ae38-4813cdceba0fLaunch the jupyter interface of your preference, notebook,
jupyter notebookor labjupyter lab
- Adams, S., & This EDS book notebook contributors. (2024). Met Office UKV high-resolution atmosphere model data (Jupyter Notebook) published in the Environmental Data Science book. Zenodo. 10.5281/ZENODO.8309345